G-quadruplexes (G4), which are special structures in DNA and RNA that play a crucial role in cells, have been associated with cancers and neurological diseases. A research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) recently built a new platform to select L-RNA aptamers that can target functional G4 structures. They found an L-RNA aptamer called L-Apt12-6 that binds specifically to a specific topology of G4 structure: parallel G4. The findings may be beneficial for developing new drugs and treatments for G4-related diseases, like cancers.
The paper, titled “Selective targeting of parallel G-quadruplex structure using L-RNA aptamer”, was published online in the prestigious journal Nucleic Acids Research.
Traditional tools, such as small molecule ligands, antibodies and peptides, have been used to target G4. However, only a handful of them can interact with particular G4 conformations. Also, the application of these tools in gene regulation, especially at the endogenous gene level, has not been extensively studied, so there is a significant research and knowledge gap. To overcome this issue, it is important to build universal platforms and novel tools that can specifically target particular G4 conformation of interest.
“As an unnatural enantiomeric form of D-RNA, L-RNA aptamer is a promising new tool for nucleic acid targeting, but its development is still in the early stages, and only a limited number of functional nucleic acid targets have been studied so far,” said Professor Chun-kit Kwok, Associate Professor in the Department of Chemistry at CityUHK, explaining the background of the research.
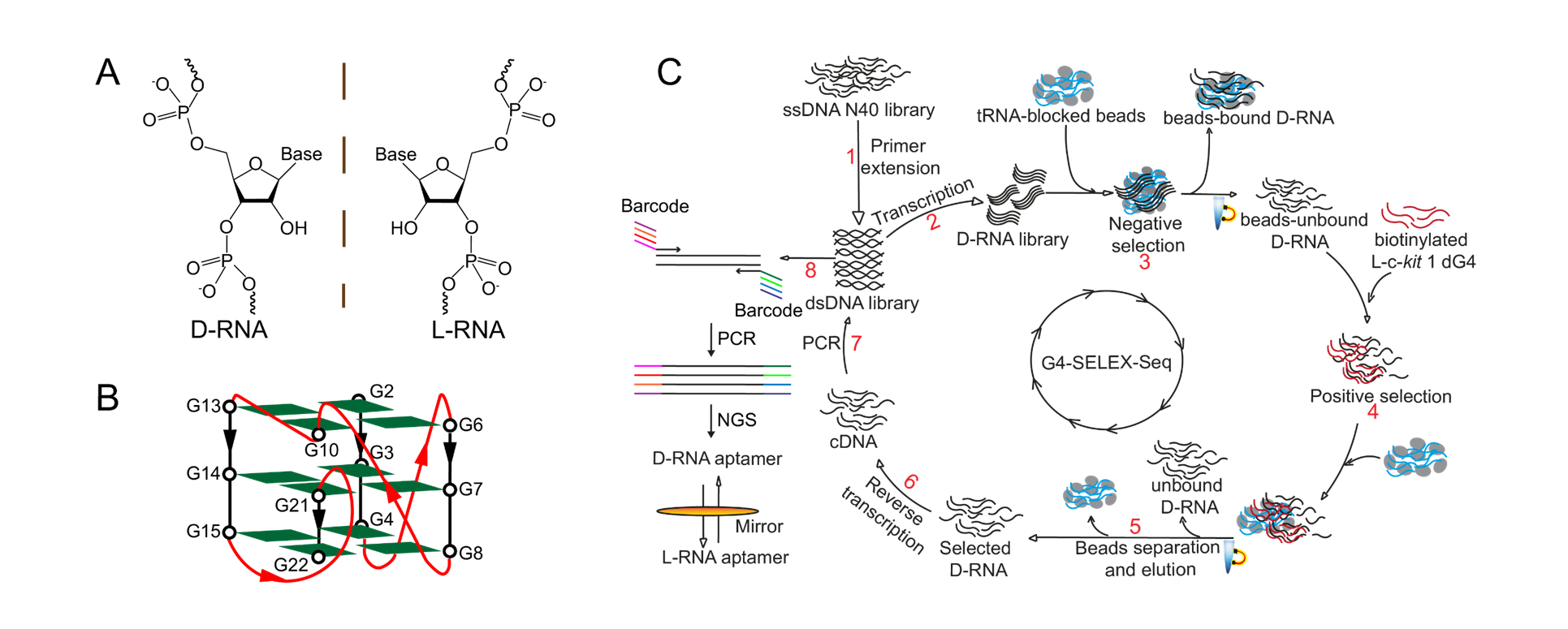
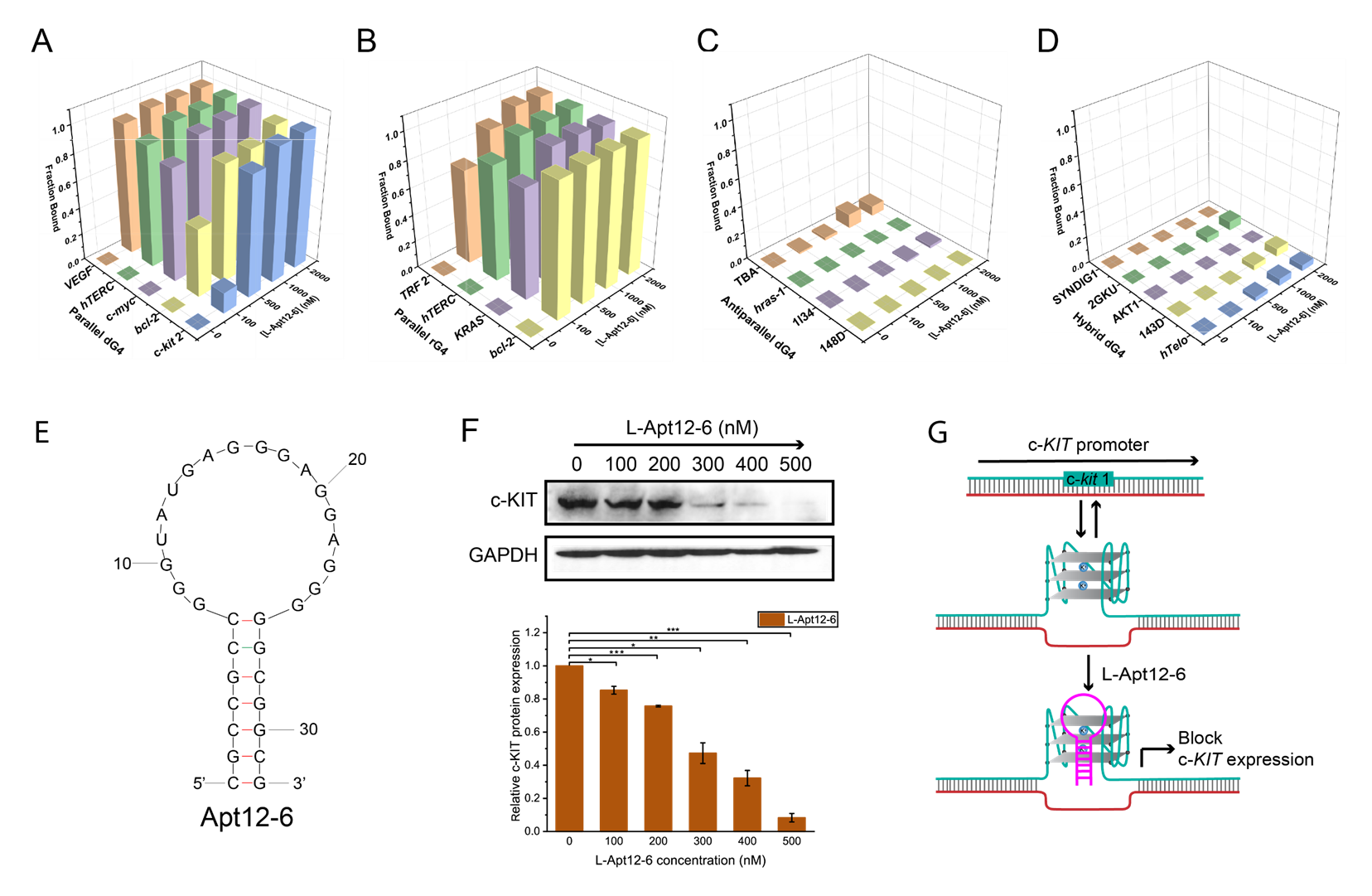
“In this study, we introduced for the first time an innovative, high-throughput L-RNA aptamer selection method, namely “G4-SELEX-Seq”, which allowed us to identify a novel L-RNA aptamer, L-Apt12-6. It binds strongly and specifically to parallel G4 over other G4 topologies and nucleic acid structures. This is the first L-RNA aptamer capable of targeting DNA G4 generally, specifically in the parallel G4 conformation. Importantly, we also demonstrated that L-Apt12-6 can control the gene expression of a proto-oncogene c-kit1 in cancer cells,” said Professor Kwok.
“We have spent over a year troubleshooting and refining the aptamer selection platform to obtain L-Apt12-6. Non-specific enrichment during SELEX hindered the selection of binding sequences.” added Dr. Danyang Ji, who is the first author in this work and currently a postdoctoral researcher in Prof. Kwok’s Lab. To overcome this, the team coupled high-throughput Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) as a readout to comprehensively analyze the enriched library. “This process is like finding a needle in a haystack!” Prof. Kwok and Dr. Ji both expressed with excitement. After multiple attempts, they were able to identify a binding candidate for their downstream applications.
“The novel SELEX strategy (G4-SELEX-Seq) can be adapted for other nucleic acid structures with appropriate refinement,” said Professor Kwok, emphasizing the potential general applications of the new strategy.
The newly discovered L-RNA aptamer, L-Apt12-6, holds significant value as a selective binder of G-quadruplex conformations. It can regulate G4-mediated gene activity both in vitro and in cells. L-Apt12-6 can be further customized by attaching various functional modules such as proteins, peptides, nucleic acids or ligands, enabling its application in a wide range of contexts including in biomedical and biotechnological areas.

For enquiry, please contact Professor Chun-kit Kwok from the Department of Chemistry at CityUHK, by email at ckkwok42@cityu.edu.hk.
This research article originated from CityUHK Research Stories.