November 25, 2023 feature
A tin-based tandem electrocatalyst for the synthesis of ethanol via CO? reduction
The electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) into various multi-carbon products is highly desirable, as it could help to easily produce useful chemicals for a wide range of applications. Most existing catalysts to facilitate CO2 reduction are based on copper (Cu), yet the processes underpinning their action remain poorly understood.
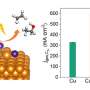
Researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, City University of Hong Kong, and other institutes in China have recently set out to design more efficient Cu-free electrochemical catalysts for the reduction of CO2 Their paper, published in Nature Energy, introduces a new catalyst based on Tin (Sn), which was found to reduce CO2 to ethanol (CH3CH2OH) with a selectivity of 80%.
"The discovery of C-C coupling over the Sn1-O3G catalyst was not accidental, but instead built on our earlier works on understanding the CO2RR behavior of transition metal single-atom catalysts," Prof. Bin Liu, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore.
"Specifically, we conducted preliminary experiments involving structural and electrochemical characterizations of various Sn-based CO2RR catalysts, including metallic Sn nanoparticles, SnS2 nanosheets, SnS2 on nitrogen-doped graphene, single Sn atoms on nitrogen-doped graphene (Sn-4N) and single Sn atoms on O-rich graphene (Sn1-O3G)."
In their preliminary experiments, the researchers found that both Sn1-4N and Sn1-O3G catalysts could reduce CO2 to CO with KHCO3, as a proton donor in a CO2RR solution. However, these catalysts displayed different behavior in the presence of the acid formate, with only Sn1-O3G ultimately producing ethanol.
"These observations led us to believe that the difference in CO2RR between the Sn1-4N and Sn1-3OG catalysts could result from the different coordination environments of Sn," Prof. Liu said. "Thereafter, we focused our efforts on understanding the C-C coupling mechanism on O-coordinated Sn catalytic sites and constructed a tandem catalyst to realize selective CO2RR to ethanol."
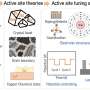
Prof. Liu and his colleagues fabricated their new Sn-based electrocatalyst by eliciting a solvothermal reaction between SnBr2 and thiourea on a three-dimensional (3D) carbon foam. They subsequently examined their catalyst to characterize its structure.
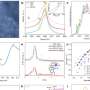
Their examinations suggest that their catalyst is made up of SnS2 nanosheets and atomically dispersed Sn atoms. These components are coordinated on the 3D O-rich carbon by binding with three O atoms (Sn1-O3G).
"The electrochemical performance of the SnS2/Sn1-O3G catalyst for CO2RR was evaluated using chronoamperometry in an H-type cell containing CO2-saturated 0.5-M KHCO3," Prof. Liu said. "Our catalyst can reproducibly yield ethanol with a Faradaic efficiency (FE) of up to 82.5% at -0.9?VRHE and a geometric current density of 17.8?mA cm–2. Additionally, the FE for ethanol production could be maintained at above 70% over the potential window from -0.6 to -1.1 VRHE."
In initial evaluations, the catalyst developed by the researchers achieved highly promising results, successfully producing ethanol from a CO2RR solution with a high selectivity. In addition, the catalyst was found to be stable, maintaining 97% of its initial activity after 100?h of operation.
"The dual active centers of Sn and O atoms in Sn1-O3G serve to adsorb different C-based intermediates, which effectively lowers the C-C coupling energy between *CO(OH) and *CHO," Prof. Liu explained. "Our tandem catalyst enables a formyl-bicarbonate coupling pathway, which not only provides a platform for C-C bond formation during ethanol synthesis and overcomes the restrictions of Cu-based catalysts but also offers a strategy for manipulating CO2 reduction pathways towards desired products."
The recent work by this team of researchers introduces an alternative Cu-free catalyst for eliciting the C-C bond formation and enabling the reduction of CO2 to ethanol. In the future, their proposed approach could be used to produce ethanol more reliably and could potentially also be applied to the synthesis of other desired chemical products via the CO2 reduction reaction.
"The search for more efficient catalysts with dual active sites should be pursued through high-throughput experiments and theoretical calculations," Prof. Liu added. "The rate and selectivity of a catalytic reaction are also closely related to the coverage of reaction intermediates on the catalyst's surface.
"Therefore, an in-depth study of factors that affect the residence time of intermediates, such as the pore structure of the support for the Sn1-O3G dual-active sites, would help to deepen understanding of the C-C coupling process. We envisage that tandem catalysis based on the concept of dual-active sites could be extendable to C-X (X?=?N or S) coupling to prepare other chemicals, such as urea and alanine."
More information: Jie Ding et al, A tin-based tandem electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction to ethanol with 80% selectivity, Nature Energy (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41560-023-01389-3
? 2023 Science X Network