Defence Against Ransomware
?
What is ransomware? [1][2]
Ransomware is a form of malicious software (malware) designed to encrypt files on a device, rendering any files and the systems that rely on them unusable. By encrypting these files and demanding a ransom payment for the decryption key, cybercriminals place individuals or organisations in a position where paying the ransom is the easiest and cheapest way to regain access to their files.
In general, there are three major operational phases of ransomware:
- Distribution and infection – The usual infection channel is that cybercriminals may send phishing emails to targeted victims with attachments containing ransomware or trick the users into clicking the link embedded in the emails. Another common infection channel is that users execute files downloaded from the Internet. Once infected, the infected computer can also propagate and infect computers on the same network.
- Data and file encryption – After ransomware has gained access to a system, it can begin encrypting its files. Since encryption functionality is built into an operating system, this involves accessing files, encrypting them with an attacker-controlled key, and replacing the originals with the encrypted versions.
- Demand for ransom – Once file encryption is completed, the ransomware is prepared to make a ransom demand. It is very common to have a display background changed to a ransom note or text files placed in each encrypted directory containing the ransom note.

Figure 1: The 3 Phases of Ransomware Attacks
What is the latest situation? [3][4]
Ransomware is among the most detrimental and widespread cyber security threats. Latest observation includes cybercriminals performing double extortion to the victims. Apart from encrypting all user files, including connected shared folders and storage devices, cybercriminals may exfiltrate sensitive information to a separate location for other purposes. For instance, if a ransom payment is not received, cybercriminals may leak the information to a public website or sell it to others.
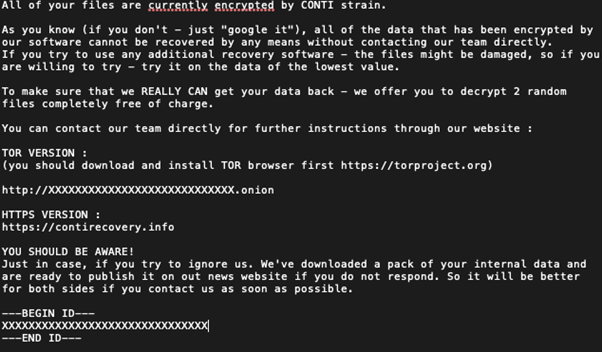
Figure 2: A sample notice of a popular Ransomware (Conti)
How does it impact us? [5][6][7]
On a personal level, the cyber-attack can lead to the loss of timely access to important data. Victims may also experience financial loss due to paying the ransom. The business could be seriously affected at the organisation level as the information system and underlying business data are no longer available for business users. An organisation's reputation could be damaged due to service unavailability, data breaches and/or potential financial penalties from regulatory authorities. Security researchers revealed that in 2021, the average ransom demand has increased by 144% over 2020. However, even if someone is willing to pay the ransom, it does not guarantee that the encrypted files can be restored to their original status. The organisation will also suffer from financial loss for business recovery.
What preventive measures can we take? [8][9]
- Install security patches to the operating system (OS) and maintain up-to-date computer software.
- Install and enable real-time protection of anti-malware software. It is worth noting that CityU staff and students are eligible to install Sophos Endpoint Protection software on their personal devices. [10]
- Perform data backup regularly and keep an offline copy.
- Do not open emails or download files from untrusted sources.
- Do not plug in and use USB devices from unknown sources.
What to do if infection is suspected?
- Immediately disconnect the infected system from the network to prevent infection propagation.
- For current CityU staff and students, please report the incident and seek proper advice from the IT Service Desk. [11]
- For the general public, affected users can report the incident to Hong Kong Computer Emergency Response Team Coordination Centre (HKCERT). [12]
- Restore data from backup to a clean device.
For enquiry related to this article, please write to infosec@cityu.edu.hk.
References
[1] https://www.cisa.gov/stopransomware
[2] https://www.checkpoint.com/cyber-hub/threat-prevention/ransomware/
[3] https://www.hkcert.org/blog/ransomware-evolved-double-extortion-and-fake-decryptor
[4] https://www.itpro.co.uk/security/ransomware/367624/the-rise-of-double-extortion-ransomware
[5] https://start.paloaltonetworks.com/unit-42-ransomware-threat-report.html
[6] https://inews.hket.com/article/3364739/
[7] https://threatpost.com/true-impact-of-ransomware-attacks/168029/
[8] https://www.infosec.gov.hk/en/best-practices/business/handling-malware-outbreak
[9] https://www.infosec.gov.hk/en/knowledge-centre/ransomware
[10] http://www.22kk77.xyz/csc/deptweb/facilities/sophos.htm
[11] http://www.22kk77.xyz/its/services-facilities/it-service-desk
[12] https://www.hkcert.org/form/incident-report-end-user-sme/entry